If you make donations to charities certified by the government, you can apply for tax credits from IRD, and the donations can be accounted for business expenses.
Learn more: Not-for-profit organisation
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you make donations to charities certified by the government, you can apply for tax credits from IRD, and the donations can be accounted for business expenses.
Learn more: Not-for-profit organisation
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you make donations to charities certified by the government, you can apply for tax credits from IRD, and the donations can be accounted for business expenses.
Learn more: Not-for-profit organisation
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Normally, if you are working on a project, it will be sold as inventory. The expenditure of developing the project will be included in Cost of Goods Sold, and it is not accounted for an expense.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Regarding the business meal expense, you can only Record 50% of the expense as a deduction because it has a significant private element. Even if you think the private element was more or less than 50% of the expense, you can only claim 50% of the expense.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Regarding the business meal expense, you can only Record 50% of the expense as a deduction because it has a significant private element. Even if you think the private element was more or less than 50% of the expense, you can only claim 50% of the expense.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to IRD, you need to file regular GST returns, and the filing frequency depends on your sales. You have to register GST if your sales were at least $60,000 in the last 12 months, or you expect it will be at least $60,000 in the next 12 months. If you have sales under $500,000 in any 12-month period, you can file GST six-monthly. If you have sales between $500,000 and $24 million in any 12-month period, you must choose to file GST two-monthly or monthly. And you must file monthly if your sales are over $24 million in any 12-month period. The sales we mentioned here are all GST inclusive.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to IRD, you need to file regular GST returns, and the filing frequency depends on your sales. You have to register GST if your sales were at least $60,000 in the last 12 months, or you expect it will be at least $60,000 in the next 12 months. If you have sales under $500,000 in any 12-month period, you can file GST six-monthly. If you have sales between $500,000 and $24 million in any 12-month period, you must choose to file GST two-monthly or monthly. And you must file monthly if your sales are over $24 million in any 12-month period. The sales we mentioned here are all GST inclusive.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The easiest way is to look at the invoice provided by the supplier. Generally speaking, exporting freight cost does not include GST, which are zero-rated GST. However, there are several types of exporting freight cost, so some of them might include GST.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The easiest way is to look at the invoice provided by the supplier. Generally speaking, exporting freight cost does not include GST, which are zero-rated GST. However, there are several types of exporting freight cost, so some of them might include GST.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 1 December 2019, GST will apply to sales of goods and services imported into New Zealand, regardless of the value. When purchasing overseas goods and services from online platforms, if the value is less than $1,000, GST will generally be collected by overseas suppliers. If the value is greater than $1,000, GST and customs duties will be collected by New Zealand Customs.
Paying withholding tax depends on whether the service is under the service category that needs to be charged. For example, a loyalty fee must be charged.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 1 December 2019, GST will apply to sales of goods and services imported into New Zealand, regardless of the value. When purchasing overseas goods and services from online platforms, if the value is less than $1,000, GST will generally be collected by overseas suppliers. If the value is greater than $1,000, GST and customs duties will be collected by New Zealand Customs.
Paying withholding tax depends on whether the service is under the service category that needs to be charged. For example, a loyalty fee must be charged.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
WT stands for withholding tax. It is generally applicable to contractors receiving scheduler payments, excluding employees receiving salary or wages. Employers withhold contractors’ personal income tax. Contractors using the tax code of WT need to fill in IR330C. In addition, the contractors will pay ACC levies by themselves rather than by the employers.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
WT stands for withholding tax. It is generally applicable to contractors receiving scheduler payments, excluding employees receiving salary or wages. Employers withhold contractors’ personal income tax. Contractors using the tax code of WT need to fill in IR330C. In addition, the contractors will pay ACC levies by themselves rather than by the employers.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The due dates of the provisional tax payments depend on which option you use and if you’re GST registered. If you use the standard or estimation option, you’ll generally pay 3 instalments of provisional tax., which are 28 August, 15 January, and 7 May. If you use accounting income method, your due dates for paying and filing your statement of activity will line up with your GST due dates. If you use the ratio option you’ll pay your provisional tax in 6 instalments, once every two months. If you pay late, underpay or fail to pay the provisional tax, you will be charged for fines and interest.
For details of provisional tax, see IR316.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The due dates of the provisional tax payments depend on which option you use and if you’re GST registered. If you use the standard or estimation option, you’ll generally pay 3 instalments of provisional tax., which are 28 August, 15 January, and 7 May. If you use accounting income method, your due dates for paying and filing your statement of activity will line up with your GST due dates. If you use the ratio option you’ll pay your provisional tax in 6 instalments, once every two months. If you pay late, underpay or fail to pay the provisional tax, you will be charged for fines and interest.
For details of provisional tax, see IR316.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Yes. With a secondary income, the tax code is S, and the tax rate is relatively high. However, if your total annual income does not increase, the overpaid taxes will be refunded at the end of a tax year.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
When your income is over $180,000, and only the excess part is taxed on 39% . You can use our Tax Calculator to calculate your income tax.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
When your income is over $180,000, and only the excess part is taxed on 39% . You can use our Tax Calculator to calculate your income tax.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to the interpretation of Children’s exempt income from IR3G, if for the tax year you were 14 or under, or were 15, 16 or 17 and still attending school, or turned 18 on or after 1 January in the previous tax year and continued to attend school.
If you receive income that has not had tax taken out before you receive it eg. worked around the home of a neighbour or family friend, and that work was not part of a business that they carry on, and your total income from these sources is less than $2,340 for the tax year, this income is exempt from tax and is not included in your return. You are not required to file a return just because you earn this type of income. If you earn $2,340 or more, the exemption does not apply and you will need to file a return and pay tax on all the income, not just the amount that exceeds the exemption.
At the same time, if there is a family business, the expenditure of $2,340/person (children’s wages) can be used as a deduction for business income. However, if this part of the annual income exceeds $2,340, you need to file all income and pay taxes.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to the interpretation of Children’s exempt income from IR3G, if for the tax year you were 14 or under, or were 15, 16 or 17 and still attending school, or turned 18 on or after 1 January in the previous tax year and continued to attend school.
If you receive income that has not had tax taken out before you receive it eg. worked around the home of a neighbour or family friend, and that work was not part of a business that they carry on, and your total income from these sources is less than $2,340 for the tax year, this income is exempt from tax and is not included in your return. You are not required to file a return just because you earn this type of income. If you earn $2,340 or more, the exemption does not apply and you will need to file a return and pay tax on all the income, not just the amount that exceeds the exemption.
At the same time, if there is a family business, the expenditure of $2,340/person (children’s wages) can be used as a deduction for business income. However, if this part of the annual income exceeds $2,340, you need to file all income and pay taxes.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The second job requires to use the Tax Code of S. The specific tax rate will vary according to the frequency and amount of salary payment. The tax can be calculated by using the PAYE calculator provided by IRD.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If it is a residential rental property, the chattel can be depreciated according to the prescribed proportion. If it is a commercial rental property, in addition to the chattel, the building can also be depreciated proportionally from the 2021 fiscal year. The specific depreciation rate can be checked through the Depreciation rate finder provided by IRD.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If it is a residential rental property, the chattel can be depreciated according to the prescribed proportion. If it is a commercial rental property, in addition to the chattel, the building can also be depreciated proportionally from the 2021 fiscal year. The specific depreciation rate can be checked through the Depreciation rate finder provided by IRD.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
As casual employees have no fixed working time, many employers are not sure how to pay public holidays for them. According to Employment NZ, the employer should firstly figure out whether or not the day of public holiday is an otherwise working day for the employee. If it is, the employer will need to use Average Daily Pay, which is a daily average of the employee’s gross earnings over the past 52 weeks. Also, if the employees work on a public holiday, they will get one time and a half of the Average Daily Pay.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
As casual employees have no fixed working time, many employers are not sure how to pay public holidays for them. According to Employment NZ, the employer should firstly figure out whether or not the day of public holiday is an otherwise working day for the employee. If it is, the employer will need to use Average Daily Pay, which is a daily average of the employee’s gross earnings over the past 52 weeks. Also, if the employees work on a public holiday, they will get one time and a half of the Average Daily Pay.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Generally, if there is a clause of compensations in the employment agreement, you need to compensate the employee according to the contract. You need to deduct PAYE for the compensation as same as salary.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Fixed-term employees have the same public holiday rights as permanent full-time and part-time employees. If they do not work on public holidays, they will be paid according to their normal working salary. If they need to work on public holidays, they will be paid 1.5 times normal salary. Causal employees generally have no wages if they do not work on public holidays, because their working hours are not fixed, so they will be paid 8% of the holiday pay with their wages.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Fixed-term employees have the same public holiday rights as permanent full-time and part-time employees. If they do not work on public holidays, they will be paid according to their normal working salary. If they need to work on public holidays, they will be paid 1.5 times normal salary. Causal employees generally have no wages if they do not work on public holidays, because their working hours are not fixed, so they will be paid 8% of the holiday pay with their wages.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Employees can ask their employer to pay out in cash, up to one week of their four weeks’ minimum entitlement to annual holidays per year for each entitlement year. They can do this all at once, or can make multiple requests to cash-up until the entire one week is cashed up. Some employees do not or rarely take annual leave, so they will negotiate with their employers and require one week of annual leave to be paid directly in the form of wages.
An employer can’t:
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Employees can ask their employer to pay out in cash, up to one week of their four weeks’ minimum entitlement to annual holidays per year for each entitlement year. They can do this all at once, or can make multiple requests to cash-up until the entire one week is cashed up. Some employees do not or rarely take annual leave, so they will negotiate with their employers and require one week of annual leave to be paid directly in the form of wages.
An employer can’t:
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Any unused sick leave at the end of a 12-month period can be carried over and added to their next year’s entitlement. The maximum amount of sick leave that can be accumulated under the Holidays Act 2003 is 20 days. The employer and employee can agree that sick leave can accumulate to more than 20 days through an employment agreement. Unused sick leave can’t be cashed-up or be part of any final payment to the employee when they leave, unless this is in the employment agreement.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Any unused sick leave at the end of a 12-month period can be carried over and added to their next year’s entitlement. The maximum amount of sick leave that can be accumulated under the Holidays Act 2003 is 20 days. The employer and employee can agree that sick leave can accumulate to more than 20 days through an employment agreement. Unused sick leave can’t be cashed-up or be part of any final payment to the employee when they leave, unless this is in the employment agreement.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Generally, when employees work for less than one year, their annual leave is accumulated at 8% of the employees’ before-tax earnings, then after one year of work, they are entitled to four weeks’ annual leave each year. If an employee wants to take annual leave before they become entitled to, it depends on if the employer allows the employee to take annual leave in advance, that is, if the ‘annual leave in advance’ item is included in the employment contract signed with the employer.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Generally, when employees work for less than one year, their annual leave is accumulated at 8% of the employees’ before-tax earnings, then after one year of work, they are entitled to four weeks’ annual leave each year. If an employee wants to take annual leave before they become entitled to, it depends on if the employer allows the employee to take annual leave in advance, that is, if the ‘annual leave in advance’ item is included in the employment contract signed with the employer.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
PAYE will not be affected. PAYE is calculated based on the employee’s tax code, payment frequency and payment amount. It can be calculated through the PAYE Calculator provided by IRD. However, casual workers are generally paid Holiday Pay together with wages due to uncertain working hours, so they are different from long-term part-time workers.
In terms of the contract, the two are generally different. Because the working hours of casual workers are not fixed, the contract may not specify fixed working hours, but part-time workers generally have fixed working hours per week, and the contract is generally noted.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
PAYE will not be affected. PAYE is calculated based on the employee’s tax code, payment frequency and payment amount. It can be calculated through the PAYE Calculator provided by IRD. However, casual workers are generally paid Holiday Pay together with wages due to uncertain working hours, so they are different from long-term part-time workers.
In terms of the contract, the two are generally different. Because the working hours of casual workers are not fixed, the contract may not specify fixed working hours, but part-time workers generally have fixed working hours per week, and the contract is generally noted.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to explanation of wage subsidies from Work and Income, if your employees’ regular wages are less than the subsidies, you must pay for their normal wages. The difference will be used to pay the wages of other affected employees. If there are no other employees, the remaining wage subsidies should be repaid to the government. The employee’s Holiday pay is calculated at 8% of the normal salary.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
According to explanation of wage subsidies from Work and Income, if your employees’ regular wages are less than the subsidies, you must pay for their normal wages. The difference will be used to pay the wages of other affected employees. If there are no other employees, the remaining wage subsidies should be repaid to the government. The employee’s Holiday pay is calculated at 8% of the normal salary.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 6 May 2019, only an employer with 19 or fewer employees (at the beginning of the day on which the employment agreement is entered into) may employ a new employee on a trial period for the first 90 calendar days of their employment. An employee can’t be on a trial period if they’ve worked for that employer before.
A valid trial period must be agreed to in the employment agreement before the employee starts work, or the trial period is invalid, and it must have a valid notice period in the employment contract.
For other conditions, please refer to Employment New Zealand.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 6 May 2019, only an employer with 19 or fewer employees (at the beginning of the day on which the employment agreement is entered into) may employ a new employee on a trial period for the first 90 calendar days of their employment. An employee can’t be on a trial period if they’ve worked for that employer before.
A valid trial period must be agreed to in the employment agreement before the employee starts work, or the trial period is invalid, and it must have a valid notice period in the employment contract.
For other conditions, please refer to Employment New Zealand.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The employer cannot choose the tax code on behalf of employee. Before the employee’s first wage payment, you need to ask the employee to fill and sign the IR330 Tax code declaration form. According to the form’s instruction, the employee will choose the right tax code by him/herself.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The employer cannot choose the tax code on behalf of employee. Before the employee’s first wage payment, you need to ask the employee to fill and sign the IR330 Tax code declaration form. According to the form’s instruction, the employee will choose the right tax code by him/herself.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you need to pay tax for the sale of residential investment properties, the tax rate is same as the individual tax rate under an individual. Under a company, the tax rate is 28%. Under a trust, the tax rate is 33%. Using which entity depends on your situation and plan. From a tax perspective, there is not much difference. Companies and trusts can also distribute profits to individuals and then pay taxes under individuals.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you need to pay tax for the sale of residential investment properties, the tax rate is same as the individual tax rate under an individual. Under a company, the tax rate is 28%. Under a trust, the tax rate is 33%. Using which entity depends on your situation and plan. From a tax perspective, there is not much difference. Companies and trusts can also distribute profits to individuals and then pay taxes under individuals.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
One of the two persons who satisfies the conditions of First-home buyer can use kiwiSaver First Home Grant without being affected by the other person.
Using the kiwiSaver First Home Grant needs to meet the conditions that the applicant does not currently own any property, use the property as main home, and has been contributing at least the minimum amount to KiwiSaver for 3 years or more, etc.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
One of the two persons who satisfies the conditions of First-home buyer can use kiwiSaver First Home Grant without being affected by the other person.
Using the kiwiSaver First Home Grant needs to meet the conditions that the applicant does not currently own any property, use the property as main home, and has been contributing at least the minimum amount to KiwiSaver for 3 years or more, etc.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Even your main home is under a trust, the sale of it can be exempted. There is no need to follow the Bright-line rule, but it also depends on the historical records of purchasing and selling main homes. If you buy and sell multiple times of main homes frequently, you will be taxed.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Even your main home is under a trust, the sale of it can be exempted. There is no need to follow the Bright-line rule, but it also depends on the historical records of purchasing and selling main homes. If you buy and sell multiple times of main homes frequently, you will be taxed.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If your family trust only has a main home, you can apply to IRD for special application to cancel the annual tax return. But if you have a rental property, you need to file taxes every year.
Although there is no need to file a tax return if there is only a main home in the trust, it is still recommended that you complete a financial report every year, because the financial report can reflect the details of the assets under the trust, which can reflect the role of the trust in protecting assets.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If your family trust only has a main home, you can apply to IRD for special application to cancel the annual tax return. But if you have a rental property, you need to file taxes every year.
Although there is no need to file a tax return if there is only a main home in the trust, it is still recommended that you complete a financial report every year, because the financial report can reflect the details of the assets under the trust, which can reflect the role of the trust in protecting assets.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The purchase and sale of main home are exempted, and there is no tax. If it is the first main home bought and sold, there is no problem for taxation, but if it is not, and there are multiple purchases and sales of main homes, there is a possibility of taxation.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The purchase and sale of main home are exempted, and there is no tax. If it is the first main home bought and sold, there is no problem for taxation, but if it is not, and there are multiple purchases and sales of main homes, there is a possibility of taxation.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
No, you don’t. As you are not GST Registered, so you don’t need to pay for GST part. But you may need to be aware of capital gain tax which will depend on your situation.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
You can apply for Wage Subsidy, but you cannot apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP), because income that is received passively, including all forms of residential and commercial rent, is excluded from the measurement of revenue in addition to IRD. If you have a rental property under individuals, and you have at least a 40% decline in rental income because you cannot renting out during the period of Lockdown. Then you can apply for Wage Subsidy as Self-employed by calculating how much time you spend managing your rental property a week.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
You can apply for Wage Subsidy, but you cannot apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP), because income that is received passively, including all forms of residential and commercial rent, is excluded from the measurement of revenue in addition to IRD. If you have a rental property under individuals, and you have at least a 40% decline in rental income because you cannot renting out during the period of Lockdown. Then you can apply for Wage Subsidy as Self-employed by calculating how much time you spend managing your rental property a week.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 9 September 2021, if you’ve been in business for at least 1 month before the alert level increase on 17 August 2021 you can apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP). It refers to the time when a company or a self-employed person starts to operate actually. If the company is only registered but has not yet started operations, then this situation does not meet the criteria. Many self-employed people will ask, “A company can check the registration time, but how should we identify the operating time?” According to our experience, if you are a self-employed person who has registered for GST, your business’s starting time is when you first file GST. If you are a self-employed person who has not registered for GST, then you can check the bank statement for the operating time for the business.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
From 9 September 2021, if you’ve been in business for at least 1 month before the alert level increase on 17 August 2021 you can apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP). It refers to the time when a company or a self-employed person starts to operate actually. If the company is only registered but has not yet started operations, then this situation does not meet the criteria. Many self-employed people will ask, “A company can check the registration time, but how should we identify the operating time?” According to our experience, if you are a self-employed person who has registered for GST, your business’s starting time is when you first file GST. If you are a self-employed person who has not registered for GST, then you can check the bank statement for the operating time for the business.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Some self-employed people and companies have received an email from Work and Income requesting additional information after applying for Wage Subsidy. We recommend that you calculate whether your turnover has fallen by 40% before replying, and the information you provide needs to be completed as much as possible, so that IRD can clearly see the decline in your income.
In most cases, the additional information required by IRD are:
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Some self-employed people and companies have received an email from Work and Income requesting additional information after applying for Wage Subsidy. We recommend that you calculate whether your turnover has fallen by 40% before replying, and the information you provide needs to be completed as much as possible, so that IRD can clearly see the decline in your income.
In most cases, the additional information required by IRD are:
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
No, you cannot use rental income to apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP), but only for Wage Subsidy. According to IRD, passive income, such as interest and dividends, and all forms of residential and commercial rent, is excluded from the measurement of revenue when applying for RSP.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
No, you cannot use rental income to apply for Resurgence Support Payment (RSP), but only for Wage Subsidy. According to IRD, passive income, such as interest and dividends, and all forms of residential and commercial rent, is excluded from the measurement of revenue when applying for RSP.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The working hours of causal staff are not fixed, the employer needs to calculate their average weekly working hours. The working hours can be calculated over the last 12 months or over the period of time they have been employed (if it’s less than 12 months). If the average working hours are 20 or more, apply for the full-time rate; if less than 20, apply for the part-time rate. After receiving the subsidy, you may pay them as their average working hours.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The working hours of causal staff are not fixed, the employer needs to calculate their average weekly working hours. The working hours can be calculated over the last 12 months or over the period of time they have been employed (if it’s less than 12 months). If the average working hours are 20 or more, apply for the full-time rate; if less than 20, apply for the part-time rate. After receiving the subsidy, you may pay them as their average working hours.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If both of these two jobs meet the criteria, the employers of these jobs can apply for Wage Subsidy using your name. If one of these jobs are self-employment, you need to apply the subsidy to that job as self-employed, and you might need to offer additional information to support your working hours every week.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If both of these two jobs meet the criteria, the employers of these jobs can apply for Wage Subsidy using your name. If one of these jobs are self-employment, you need to apply the subsidy to that job as self-employed, and you might need to offer additional information to support your working hours every week.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
It depends on whether you file PAYE for the new employee or not. If you have never filed PAYE for him/her before moving to lockdown, it is possible that the subsidy cannot be approved because IRD does not have any information from him/her.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
It depends on whether you file PAYE for the new employee or not. If you have never filed PAYE for him/her before moving to lockdown, it is possible that the subsidy cannot be approved because IRD does not have any information from him/her.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
When applying for Wage Subsidy, there are two application links, one is Employer (for employer with employees) and another one is Self-employed (for employer without employees, i.e. self-employed). If you usually do not file PAYE for yourself, but get Shareholder Salary at the end of financial years and have employees, you can apply through the Employer link and fill both your employees and yourself in Employee List. If you have no employees, apply through the Self-employed link and fill in your company and personal information.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
When applying for Wage Subsidy, there are two application links, one is Employer (for employer with employees) and another one is Self-employed (for employer without employees, i.e. self-employed). If you usually do not file PAYE for yourself, but get Shareholder Salary at the end of financial years and have employees, you can apply through the Employer link and fill both your employees and yourself in Employee List. If you have no employees, apply through the Self-employed link and fill in your company and personal information.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
During the period of lockdown, after receiving the Wage Subsidy under the name of employees, it is generally necessary to pay the employees with their usual wages. According to Work and Income, employers must use their best endeavours to pay the employee named in the application at least 80% of their usual wages. However, if a employee does not work and does not want to take annual leave, and the employee’s usual wage is higher than the amount of the subsidy, you can only give the amount of subsidy to the employee. You should negotiate with the employee about how to giving the subsidy and keep a record in a written form.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
During the period of lockdown, after receiving the Wage Subsidy under the name of employees, it is generally necessary to pay the employees with their usual wages. According to Work and Income, employers must use their best endeavours to pay the employee named in the application at least 80% of their usual wages. However, if a employee does not work and does not want to take annual leave, and the employee’s usual wage is higher than the amount of the subsidy, you can only give the amount of subsidy to the employee. You should negotiate with the employee about how to giving the subsidy and keep a record in a written form.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Different from RSP using an actual revenue decline, Wage Subsidy can use a predicted revenue decline. Thus, if you predicted a 40% decline in revenue that did not eventuate, you need to inform Work and Income within 5 working days to repay the subsidy. We also recommend you prepare the evidence of actual revenue as much as possible before you make the application.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Different from RSP using an actual revenue decline, Wage Subsidy can use a predicted revenue decline. Thus, if you predicted a 40% decline in revenue that did not eventuate, you need to inform Work and Income within 5 working days to repay the subsidy. We also recommend you prepare the evidence of actual revenue as much as possible before you make the application.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Each time IRD open the application for RSP lasting 28 days, you can apply once. For example, the application opening on August, you can apply once. Next month, the application is opend again, you also can apply once. Within the opening period, if you meet the criteria, you can apply for RSP once.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Each time IRD open the application for RSP lasting 28 days, you can apply once. For example, the application opening on August, you can apply once. Next month, the application is opend again, you also can apply once. Within the opening period, if you meet the criteria, you can apply for RSP once.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you meet the criteria, you can apply for Covid-19 financial supports as a self-employed person, including Wage Subsidy and Resurgence Support Payment (RSP). For RSP, you must have been in business for at least 6 months and have evidence to support that. For example, if you are a sole trader who has registered for GST, you can use GST Return to support your business time.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If you meet the criteria, you can apply for Covid-19 financial supports as a self-employed person, including Wage Subsidy and Resurgence Support Payment (RSP). For RSP, you must have been in business for at least 6 months and have evidence to support that. For example, if you are a sole trader who has registered for GST, you can use GST Return to support your business time.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Different from RSP using an actual revenue decline, Wage Subsidy can use a predicted revenue decline. Thus, if you predicted a 40% decline in revenue that did not eventuate, you need to inform Work and Income within 5 working days to repay the subsidy. We also recommend you prepare the evidence of actual revenue as much as possible before you make the application.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Different from RSP using an actual revenue decline, Wage Subsidy can use a predicted revenue decline. Thus, if you predicted a 40% decline in revenue that did not eventuate, you need to inform Work and Income within 5 working days to repay the subsidy. We also recommend you prepare the evidence of actual revenue as much as possible before you make the application.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The benefits received by individuals, such as Working for Families, are related to family income. The company is an independent entity, so the company’s profit and loss is not related to the family and the individual, and it will not affect personal benefit.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
The benefits received by individuals, such as Working for Families, are related to family income. The company is an independent entity, so the company’s profit and loss is not related to the family and the individual, and it will not affect personal benefit.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Yes, although a company may not hire employees, you, as a shareholder and a director, run the company, so you are actually the employee of your company. You also receive shareholder salary, so you need to pay ACC.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
A business name is the name that a company needs to officially register on the Company Office. A trading name is used for customers when doing business, and does not need to be registered. For avoiding malicious use of the same trading name by other businesses, you can protect it by registering and applying for Trademark.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
A business name is the name that a company needs to officially register on the Company Office. A trading name is used for customers when doing business, and does not need to be registered. For avoiding malicious use of the same trading name by other businesses, you can protect it by registering and applying for Trademark.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Regarding the tax residency status for individuals, it uses either the 183-day rule or the determination of whether you have a permanent place of abode in New Zealand.
The factors like having New Zealand nationality, having a bank account in New Zealand and contributing KiwiSaver will be considered when determining whether you have a permanent place of abode in New Zealand, but they are not certain factors. It will consider your other conditions.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Regarding the tax residency status for individuals, it uses either the 183-day rule or the determination of whether you have a permanent place of abode in New Zealand.
The factors like having New Zealand nationality, having a bank account in New Zealand and contributing KiwiSaver will be considered when determining whether you have a permanent place of abode in New Zealand, but they are not certain factors. It will consider your other conditions.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If the Company Office displays the “overdue” information, you need to submit the Company Annual Return as soon as possible. If you do nothing, your company will be forced to de-registration. If your company has unresolved tax issues, IRD will punish you.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
If the Company Office displays the “overdue” information, you need to submit the Company Annual Return as soon as possible. If you do nothing, your company will be forced to de-registration. If your company has unresolved tax issues, IRD will punish you.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Yes, the bank will charge interest tax. If you are not a New Zealand tax resident, you can apply for NRWT or AIL from the bank, and the interest tax is relatively low. The AIL tax rate is only 2%, which is lower than NRWT. For countries that have signed the DTA, this part of the tax is not tax deductible in the depositor’s tax resident country, but NRWT is tax deductible.
However, if you are a New Zealand tax resident, you must choose a RWT rate based on your annual income.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Yes, the bank will charge interest tax. If you are not a New Zealand tax resident, you can apply for NRWT or AIL from the bank, and the interest tax is relatively low. The AIL tax rate is only 2%, which is lower than NRWT. For countries that have signed the DTA, this part of the tax is not tax deductible in the depositor’s tax resident country, but NRWT is tax deductible.
However, if you are a New Zealand tax resident, you must choose a RWT rate based on your annual income.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
It depends on whether foreign people are tax residents of New Zealand or not. If you are a New Zealand tax resident, you need to file not only your income in New Zealand, but also your overseas income. If you are not a New Zealand tax resident, you only need to file your income in New Zealand to IRD.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
It depends on whether foreign people are tax residents of New Zealand or not. If you are a New Zealand tax resident, you need to file not only your income in New Zealand, but also your overseas income. If you are not a New Zealand tax resident, you only need to file your income in New Zealand to IRD.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
There is currently no way to search the company’s address for service by the name of the company’s directors.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Under normal circumstances, the restaurant’s trading address will be displayed in the “Address for service” of Company Office, as shown in the figure below.
If the displayed address is incorrect, it is possible that the registrant has not completed the company information, and there is no other way to check it. However, you can also try to make a search using Google through Trading name (if available) for reference. You can see the trading name of the company as shown in the figure below, but if it is not provided, it is difficult to find it in other ways.
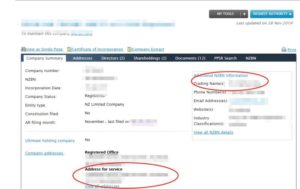
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Under normal circumstances, the restaurant’s trading address will be displayed in the “Address for service” of Company Office, as shown in the figure below.
If the displayed address is incorrect, it is possible that the registrant has not completed the company information, and there is no other way to check it. However, you can also try to make a search using Google through Trading name (if available) for reference. You can see the trading name of the company as shown in the figure below, but if it is not provided, it is difficult to find it in other ways.

This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
In general, most benefits in New Zealand will be paid after tax deductions. Moreover, the GCAP is generally paid directly to the early childhood education center, rather than directly to the parents.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Log in to myIR, click “Income Tax”, and select “Opt-in to carry-back loss” in the box of “I want to…” in the upper right corner to enter the application page. There are two years to choose from, which are the 18-19 fiscal year and the 19-20 fiscal year. Assuming that the loss was incurred in 2020, and that it was profitable in 2019 and the income tax has been paid, then the loss in 2020 can be used to deduct the profit of 2019 in this way, and then the income tax that has been paid is refunded. If there will be a loss in 2021, the profit in 2020 can also be deducted in this way and the corresponding income tax will be refunded.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Log in to myIR, click “Income Tax”, and select “Opt-in to carry-back loss” in the box of “I want to…” in the upper right corner to enter the application page. There are two years to choose from, which are the 18-19 fiscal year and the 19-20 fiscal year. Assuming that the loss was incurred in 2020, and that it was profitable in 2019 and the income tax has been paid, then the loss in 2020 can be used to deduct the profit of 2019 in this way, and then the income tax that has been paid is refunded. If there will be a loss in 2021, the profit in 2020 can also be deducted in this way and the corresponding income tax will be refunded.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This is a tax called resident withholding tax that the bank has an obligation to withhold from certain payments of investment income such as interest or dividends. You can choose the RWT rate from the following rates 10.5%, 17.5%, 28%, 30%, 33% which is determined by your annual income.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This is a tax called resident withholding tax that the bank has an obligation to withhold from certain payments of investment income such as interest or dividends. You can choose the RWT rate from the following rates 10.5%, 17.5%, 28%, 30%, 33% which is determined by your annual income.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Annual return is different thing from a financial report. The Companies Register has general information record that the public can have access to view. If you are running a company, you must update the company’s information each year through an annual return.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
Annual return is different thing from a financial report. The Companies Register has general information record that the public can have access to view. If you are running a company, you must update the company’s information each year through an annual return.
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文
This page is also available in:
 简体中文
简体中文